Natural fibers are renewable, which means they can grow again to replace the old fibers of the past. Polyethylene and other synthetic fibers are obtained after industrial processing of oil. They are non renewable fossil energy.
Wool is produced from nearly 500000 pastures in more than 100 countries. Sheep (bovine family, sheep subfamily) continue to produce wool, so the pasture usually shears the sheep once a year. Australia is a well deserved land of merino wool, producing nearly 60% of clothing wool and 90% of fine clothing wool.

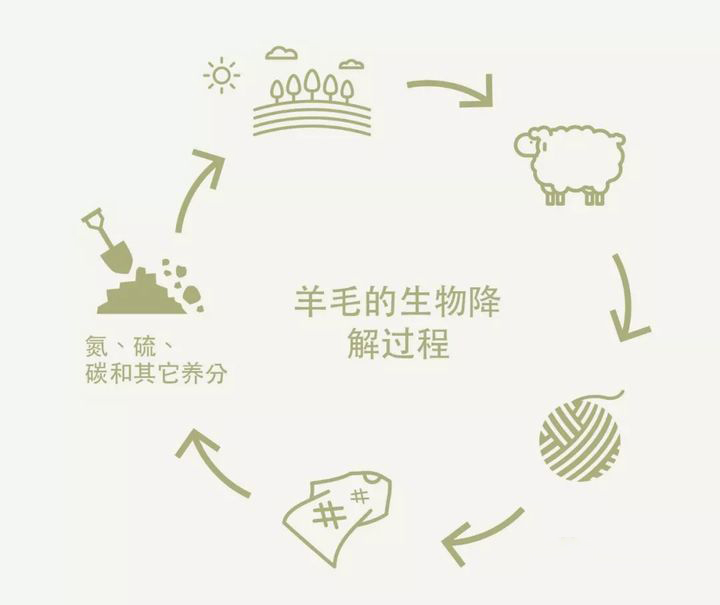
Wool is 100% biodegradable. When the service life of wool clothing ends, wool fiber will degrade and release nutrients back to the soil. See a brief introduction to wool biodegradability.
Characteristics of wool fiber
For thousands of years, natural fiber has been used by human civilization. They are either made into clothes for wearing, or used to decorate people's living environment to bring warmth and comfort. The history of wool knitted fabrics found in Denmark can be traced back to 1500 BC. Today, wool still enjoys the reputation of "global high-quality textile fiber" with its outstanding performance.
Natural curl and scale structure make wool fiber easier to hold, which is conducive to spinning. The moisture absorption and perspiration performance of wool can protect sheep from natural disasters, and also make wool clothes comfortable to wear at different temperatures. It is worth mentioning that the strength, temperature and humidity management and odor resistance of wool make this traditional fiber shine in the field of innovation and be used in high-performance sportswear, health products and industrial textiles.
Natural and renewable fibers are the best choice for environmental protection
Different from man-made fibers processed by non renewable fossil energy, natural fibers are formed by the natural transportation of natural components. For example, wool is the fiber obtained by the natural transportation of water, air, sunlight and grass.
Among the mainstream clothing fibers, wool is one of the most reusable and recycled fibers. Wool has a long service life and can be recycled and made into new textiles and clothing, durable indoor decorations or natural fire-proof products with high ignition point, which also makes the environmental protection characteristics of wool fiber more outstanding. In addition to being processed into high-end skin friendly clothing, wool also has many industrial uses, including wool for temperature and sound insulation and oil absorbing wool felt for oil spill treatment.
After being discarded, natural fibers such as wool are not easy to cause pollution and garbage accumulation. Under warm and humid conditions such as soil, wool will degrade rapidly after the action of fungi and bacteria, release nutrients (such as nitrogen and sulfur), enter the carbon and nutrient cycle of nature, and provide energy for the growth of organic matter.